Sport and Competition
People Playing Pickleball Who End Up in the Emergency Room
A new study highlights pickleball injuries.
Posted March 5, 2024 Reviewed by Ray Parker
Key points
- Pickleball-related injuries are more common than previously thought.
- The most common types of pickleball-related injuries are fractures, sprains, and internal organ injuries.
- One in five injuries required hospitalization, primarily due to cardiac arrest or fractures.
There are roughly 8.9 million pickleball players out there today. But how many of them get sent to the emergency room? And in what ways could this actually happen?
A new study by Ches Jones and Bart Hammig of the University of Arkansas published in Health sought to figure this out by looking at emergency room data. The study, titled The Role of Age as a Risk Factor for Pickleball-related Injuries, examined data from the National Electronic Injury Surveillance System (NEISS), which collects data from a sample of 100 U.S. emergency departments. The authors looked at the most recent year of data and searched for “pickleball” (injury code 3235 in the NEISS database).
According to the authors:
“There were 296 records that were identified as ‘pickleball related’ injury incidents from U.S. emergency rooms for 2022. Using the weight variable projected the number of emergency room visits from pickleball-related injuries in 2022 (was) 17,416 injuries. The results presented that close to 87% of all injuries reported were from participants over age 50.
The most common diagnosis was for fractures at 30%, followed by sprains at 17% and internal organ injury (7.2%). There were 29% of cases that did not state the diagnosis for the injury. As far as body region most impacted, the upper trunk (17%) was the most common location followed by lower trunk (10%) and then head (10%). One of five injury cases was treated and admitted for hospitalization. Most of the hospital admissions were for cardiac arrest, with the other 25% admitted for fractures. Of the 296 records there was one recorded death due to cardia arrest. No reports recorded alcohol use from the related incidents.”
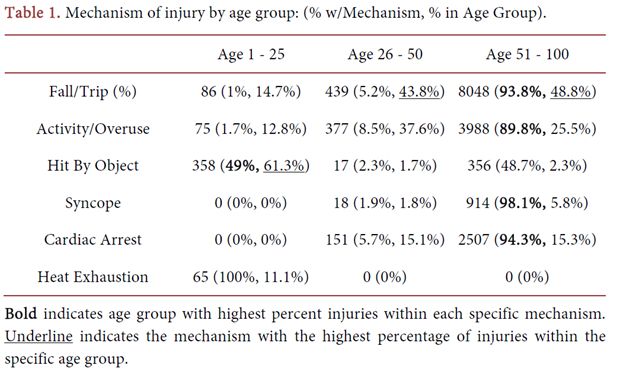
The majority of older people end up in the emergency room due to cardiac arrest, “syncope” (fainting or passing out), falling or tripping, or activity and overuse. However, roughly equal numbers of younger and older people were “hit by (an) object,” and all reported heat exhaustion cases were from younger people.
References
Jones, C., & Hammig, B. (2024). The role of age as a risk factor for pickleball-related injuries. Health, 16, 87-91.


